Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
You are given the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only.
Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number.
For example, the root-to-leaf path 1 -> 2 -> 3 represents the number 123.
Return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. Test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.
A leaf node is a node with no children.
Example 1:
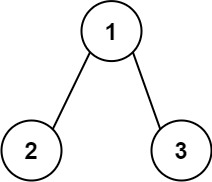
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
Example 2:
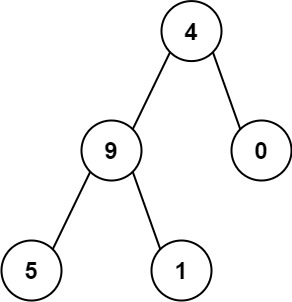
Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
0 <= Node.val <= 9
The depth of the tree will not exceed 10.
Approach: DFS (Depth First Search)
Steps:
-
Start from the root.
-
Pass the current number so far down the path.
-
At each node:
current = current * 10 + node.val -
When you reach a leaf, return the number.
-
Recursively calculate left and right subtree sum
Comments
Post a Comment