You are given the root node of a binary search tree (BST) and a value to insert into the tree. Return the root node of the BST after the insertion. It is guaranteed that the new value does not exist in the original BST.
Notice that there may exist multiple valid ways for the insertion, as long as the tree remains a BST after insertion. You can return any of them.
Example 1:
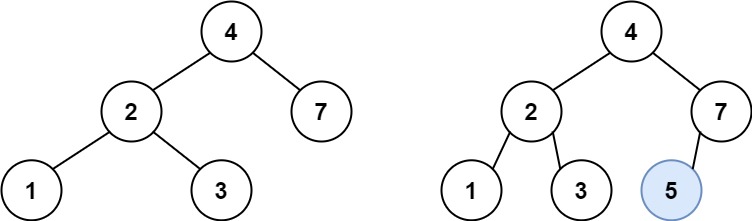
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5]
Explanation: Another accepted tree is:
Example 2:
Input: root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
Output: [40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
Example 3:
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5]
Recursive Approach (Simple & Clean)
🔹 Steps:
-
If root is null, create a new node with the given value.
-
If val < root.val, go to the left subtree.
-
If val > root.val, go to the right subtree.
-
At the correct position (null child), insert a new node.
-
Return the root.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// Base Case: If tree is empty or found null spot
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
// If value is less than current node → insert left
if (val < root.val) {
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
}
// If value is greater than current node → insert right
else if (val > root.val) {
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
}
// Return the unchanged root node pointer
return root;
}
}
Java Code (Iterative version)
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode current = root;
while (true) {
if (val < current.val) {
if (current.left == null) {
current.left = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}
current = current.left;
} else { // val > current.val
if (current.right == null) {
current.right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}
current = current.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}


Comments
Post a Comment