Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
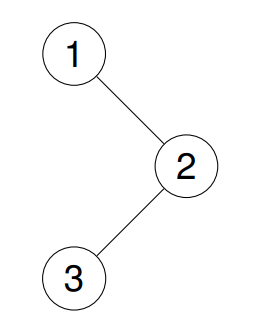
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:
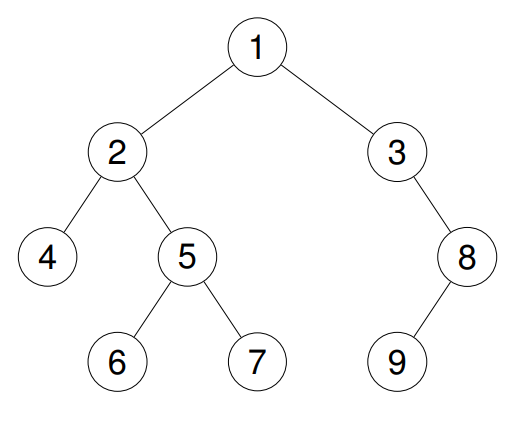
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,6,7,5,2,9,8,3,1]
Explanation:
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Steps (Recursive Approach)
-
Traverse left subtree
-
Traverse right subtree
-
Process current node (root)
Java Code: Iterative Postorder Using 2 Stacks
Option 1: Using Two Stacks
This is the most intuitive and interview-safe iterative method.
🧠 Approach Summary (Two Stack Trick):
-
Push root into stack1
-
Pop from
stack1, push intostack2 -
Push left, then right into
stack1 -
At the end, stack2 will have root-right-left, so reverse = postorder
🔁 Why This Works?
-
We push
root→right→leftintostack1 -
And pop into
stack2 -
So
stack2= root-right-left → reverse it = left-right-root (postorder)
Comments
Post a Comment