Path Sum
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
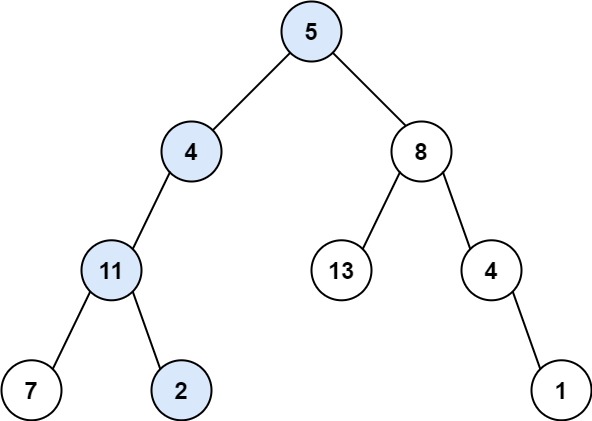
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There are two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
Output: false
Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
🔄 Dry Run Step-by-Step (DFS Style):
Call: hasPathSum(5, 22)
-
Node = 5
-
Remaining = 22 - 5 = 17
Now explore both left and right:
▶ Left Subtree of 5: hasPathSum(4, 17)
-
Node = 4
-
Remaining = 17 - 4 = 13
▶ Left Subtree of 4: hasPathSum(11, 13)
-
Node = 11
-
Remaining = 13 - 11 = 2
→ Left Subtree of 11: hasPathSum(7, 2)
-
Node = 7 (leaf)
-
Check: 2 == 7? ❌
-
Return false
→ Right Subtree of 11: hasPathSum(2, 2)
-
Node = 2 (leaf)
-
Check: 2 == 2?
-
Return true
→
hasPathSum(11, 13) = true→
hasPathSum(4, 17) = true→
hasPathSum(5, 22) = true How It "Decides" Path:
-
It tries all paths using recursion.
-
If any of them is valid, it returns
true. -
No path is “chosen” ahead — it's exploration via DFS.
Comments
Post a Comment