Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
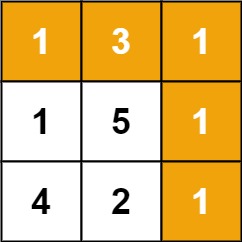
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
Output: 12
Constraints:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 200
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 200
class Solution {
public int solve(int i,int j,int m,int n, int [][] dp,int[][] Grid){
if(i==m-1 && j==n-1)
{
return Grid[i][j];
}
if(dp[i][j] !=-1)
{
return dp[i][j];
}
if(i==m-1)
{
return Grid[i][j]+solve(i,j+1,m,n,dp,Grid);//right move only
}
else if(j==n-1)
{
return Grid[i][j]+solve(i+1,j,m,n,dp,Grid);//down move only
}
else
{
int right=solve(i,j+1,m,n,dp,Grid);
int down=solve(i+1,j,m,n,dp,Grid);
dp[i][j]=Grid[i][j]+Math.min(right,down);
return dp[i][j];
}
}
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
int row=grid.length;
int col=grid[0].length;
int [][] dp= new int[row][col];
// Initialize all cells to -1 (uncomputed)
for (int m = 0; m < row; m++) {
for (int n = 0; n < col; n++) {
dp[m][n] = -1;
}
}
return solve(0,0,row,col,dp,grid);
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment