Search a 2D Matrix II LeetCode
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value target in an m x n integer matrix matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left to right.
Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top to bottom.
Example 1:
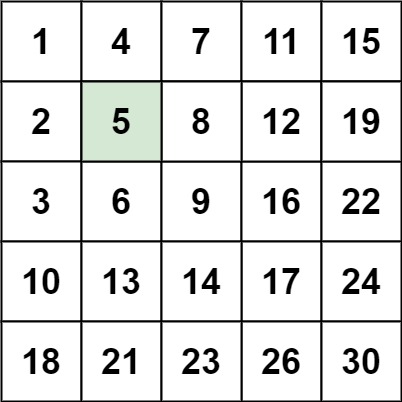
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
Output: true
Example 2:
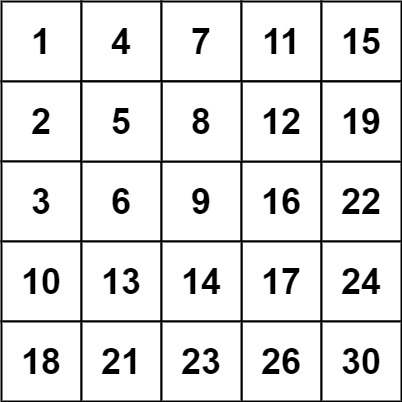
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
Output: false
Approach Used (Search from Top-Right Corner)
-
Start from the top-right corner of the matrix
(row = 0, col = last index). -
Compare the element with the target:
-
If it matches, return
true. -
If the target is smaller, move left (decrease
col). -
If the target is larger, move down (increase
row).
-
-
Continue this process until either:
-
The element is found (
return true). -
The indices go out of bounds (
return false).
-
Time Complexity:
-
O(m + n) → At worst, we traverse
mrows andncolumns once.
This is an efficient approach for searching in a sorted 2D matrix. 🚀
Comments
Post a Comment