Reshape the Matrix LeetCode
In MATLAB, there is a handy function called reshape which can reshape an m x n matrix into a new one with a different size r x c keeping its original data.
You are given an m x n matrix mat and two integers r and c representing the number of rows and the number of columns of the wanted reshaped matrix.
The reshaped matrix should be filled with all the elements of the original matrix in the same row-traversing order as they were.
If the reshape operation with given parameters is possible and legal, output the new reshaped matrix; Otherwise, output the original matrix.
Example 1:
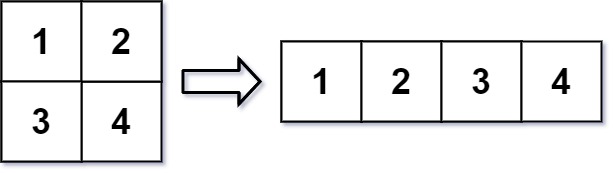
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 1, c = 4
Output: [[1,2,3,4]]
Example 2:

Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 2, c = 4
Output: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Code :
class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] mat, int r, int c) {
// Get the number of rows and columns in the original matrix
int row = mat.length;
int col = mat[0].length;
// If reshaping is not possible, return the original matrix
if (row * col != r * c) {
return mat;
}
// Create a new matrix with the required dimensions (r x c)
int[][] reshapmatrix = new int[r][c];
// Traverse through each element in the original matrix and place it in the reshaped matrix
for (int i = 0; i < row * col; i++) {
// Compute new row index in the reshaped matrix using i / c
// Compute new column index using i % c
reshapmatrix[i / c][i % c] = mat[i / col][i % col];
}
// Return the newly reshaped matrix
return reshapmatrix;
}
}
Code :
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Codefile {
public static List<List<Integer>> solve(List<List<Integer>> input, int r, int c) {
// Get the number of rows and columns in the original matrix
int row = input.size();
int col = input.get(0).size();
// If reshaping is not possible, return the original matrix
if (row * col != r * c) {
return input;
}
// Create a new matrix with r rows and initialize each row as an empty list
List<List<Integer>> reshapeMatrix = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
reshapeMatrix.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// Traverse through each element in the original matrix and place it in the reshaped matrix
for (int i = 0; i < row * col; i++) {
// Compute the new row index for the reshaped matrix
int new_row = i / c;
// Compute the new column index for the reshaped matrix
int new_column = i % c;
// Extract the value from the original matrix using row-major order
int value = input.get(i / col).get(i % col);
// Add the value to the appropriate row in the reshaped matrix
reshapeMatrix.get(new_row).add(value);
}
// Return the newly reshaped matrix
return reshapeMatrix;
}
}
Code :-
class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] mat, int r, int c) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
// Check if reshaping is possible
if (m * n != r * c) {
return mat; // Return the original matrix
}
int[][] reshapedMatrix = new int[r][c];
int row = 0, col = 0;
// Fill the reshaped matrix
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
reshapedMatrix[row][col] = mat[i][j];
col++;
if (col == c) {
col = 0;
row++;
}
}
}
return reshapedMatrix;
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment